Week 14 - Day 3 (Ch2 pt 2 Personality)
Navigate using audio
Anouncements
Final
- Friday, May 6th 11:30AM - 2PM
- Same room different time
- Same length as previous tests
- Take make up exams directly after
Personality
Stages of Psychosexual Development
Oral Stage (birth – 18 months)
- Conflict = the weaning process
- The child must become less dependent upon caretakers
- Stingy mom -> fixation -> oral character = pessimism, envy, suspicion and sarcasm, trust issue Over indulgent mom fixation oral character = optimistic, gullible, and is full of admiration for others, dependency issues
- Oral fixation can result in problems with drinking, eating, smoking, or nail biting
Anal Stage (2-3 years)
- Conflict = toilet training
- The child has to learn to control his or her bodily needs
- Developing this control leads to a sense of accomplishment and independence
- Success depends on the parents’ approach
- Parents who utilize praise and rewards encourage positive outcomes and help children feel capable and productive
- Parents too lenient fixation anal-expulsive personality = a messy wasteful or destructive personality
- Parents too strict or begin toilet training too early fixation anal-retentive personality = a stringent, orderly, rigid and obsessive personality
Phallic Stage (3-5 years)
- Conflict = Oedipus complex, Electra complex, castration anxiety, penis envy
- “I’m going to marry Daddy (Mommy) when I grow up”
- Boys: castration anxiety causes boys to reject desires for their mother, adopt father’s standards of conscience and morality
- Audio 0:14:52.338525
- The idea that a young boy seeing a naked woman would think they were castrated and then act like their dad out of fear
- Girls: have no motivation (i.e., fear of castration) to identify strongly with either parent, thus develop strong superego
- Not learning to identity with parent of same sex Fixation phallic character = reckless, resolute, self-assured, and narcissistic (excessively vain and proud)
- Can cause a person to be afraid or incapable of close love
Latency Period (6-puberty)
- No conflict
- Libido is suppressed
- Ego and superego develop more
- Important in the development of social and communication skills and self-confidence
Genital Stage (puberty-death)

- No conflict
- Goal = to become a well balanced, healthy person
- Individuals develops sexual interest
- Growing interest in welfare of others
- If all stages completed successfully, individuals should be well-balanced, warm and caring
- If fixated at any early stage, development will be troubled, with further struggle with repression and defenses.
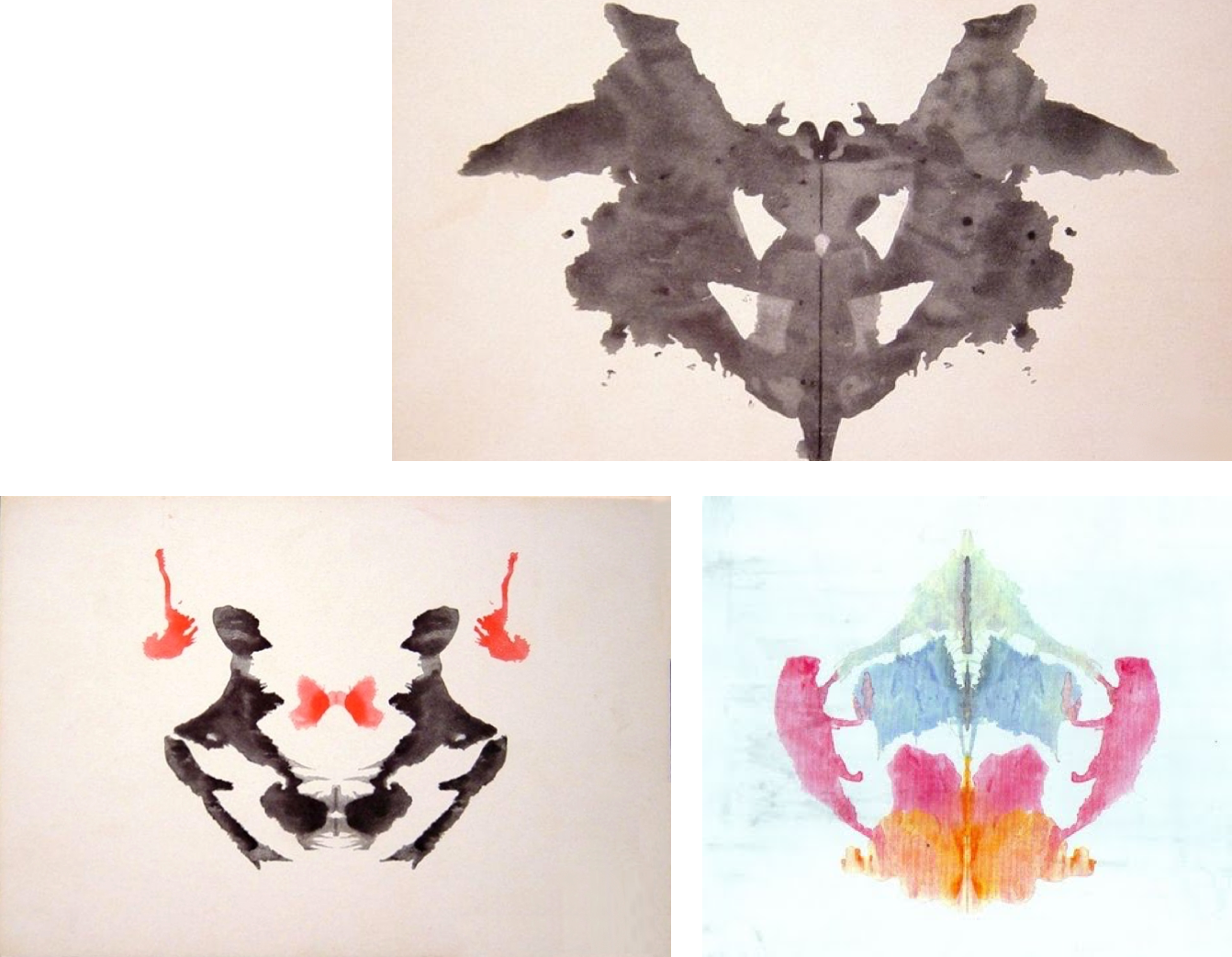
Projective Measures
- Personality tests that examine unconscious processes by having people interpret ambiguous stimuli
- Based in psychodynamic theory
- Examples
- Rorschach inkblot test
- Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
- The general idea is that people will reveal hidden aspects of personality such as motives, wishes, and unconscious conflicts
Thermic Apperception Test (TAT)
Humanistic Approach
- Seeks to understand personality by focusing on how people seek to fulfill their potential through greater self-understanding
- Audio 0:26:33.862427
- Features of Humanist Approaches
- Emphasizes personal experience
- Considers belief systems
- Views humans as unique
- Sees humans as basically good
- Abraham Maslow
- Peak experiences: rare moments of rapture caused by the attainment of excellence or the experience of beauty
- Self-actualization: striving for a life that is meaningful, challenging, and satisfying
Carl Roger’s Humanistic Theory of Personality
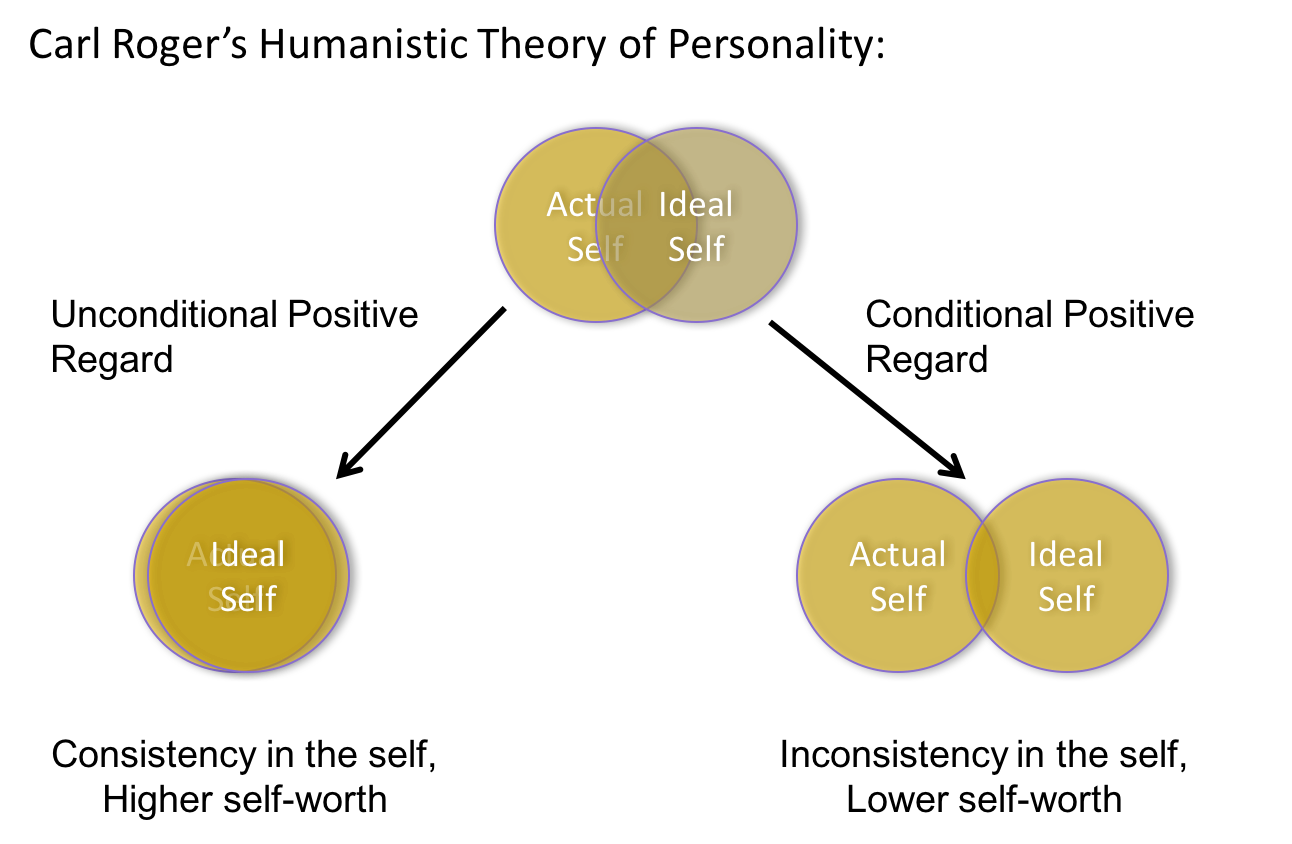
- Audio 0:28:49.213278
- Describes processes which lead to you becoming the best version of you
Objective Measures
- Relatively direct assessments of personality, usually based on information gathered through self-report questionnaires or observer ratings
- Require written responses
- Often a large inventory of traits:
- Myers-Briggs (types)
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Trait approaches: focus on how individuals differ in personality dispositions, such as sociability, cheerfulness, and aggressiveness
- Audio 0:32:04.803851
- Early Models: Eysenck’s Hierarchical Model
- The basic structure of this model included:
- Specific response level
- Habitual response level
- Superordinate traits
- Introversion/extraversion
- Emotional stability
- Audio 0:32:32.539550
- Psychoticism (i.e., constraint)
- The basic structure of this model included:
The Big Five
- Five-factor model: identifies five basic personality traits
- For each factor, there is a continuum from low to high
- Each factor is a higher-order trait that is made up of interrelated lower-order traits
- People’s “scores” on the Big Five traits have been shown to predict a wide variety of different behaviors (e.g., conscientiousness predicts grades in college)
- The Big Five approach currently dominates how many psychologists study personality
- Audio 0:33:52.799695
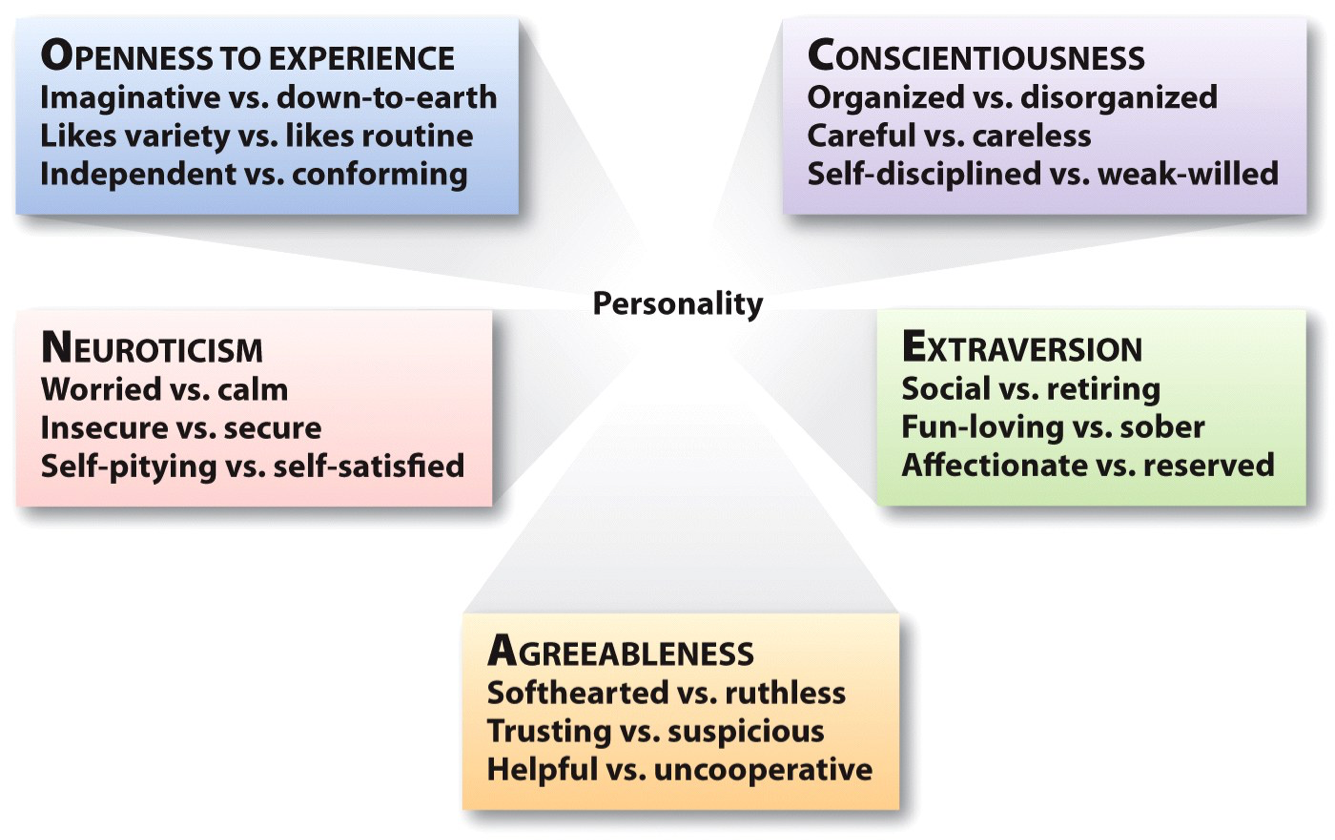
O.C.E.A.N.
- Openness to Experience
- The breadth, depth, originality, and complexity of an individual’s mental and experiential life
- Conscientiousness
- Socially prescribed impulse control that facilitates task- and goal-oriented behavior
- Audio 0:35:17.980912
- Socially prescribed impulse control that facilitates task- and goal-oriented behavior
- Extraversion
- An energetic approach to the social and material world
- Agreeableness
- A prosocial and communal orientation toward others
- Neuroticism
- The opposite of emotional stability and even-temperedness
- Relatively consistent across populations
- Specific patterns of change over time
- The maturity principle: increases in agreeableness and conscientiousness, decreases in neuroticism into middle age
- Audio 0:38:21.171625
- We become more mature, less neurotic, etc.
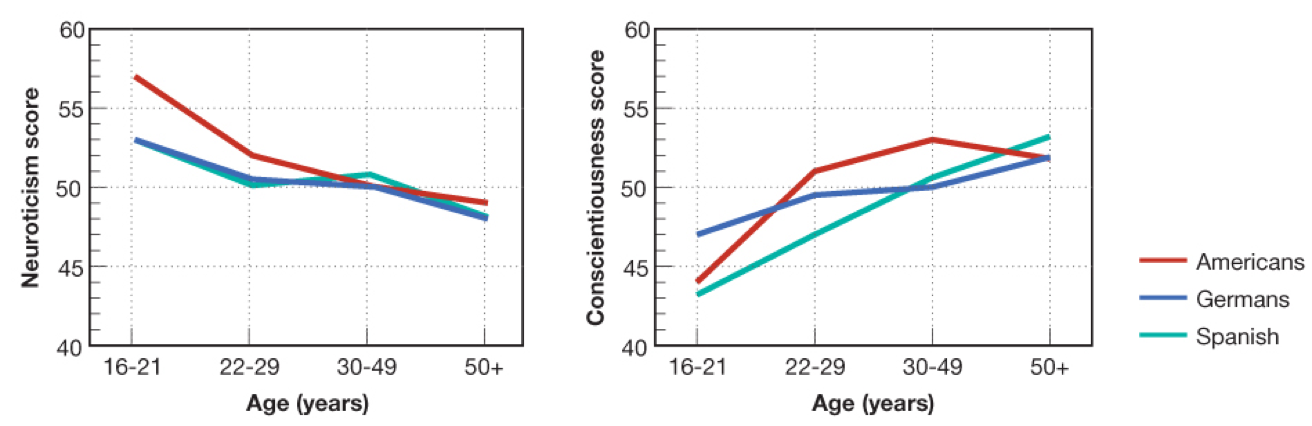
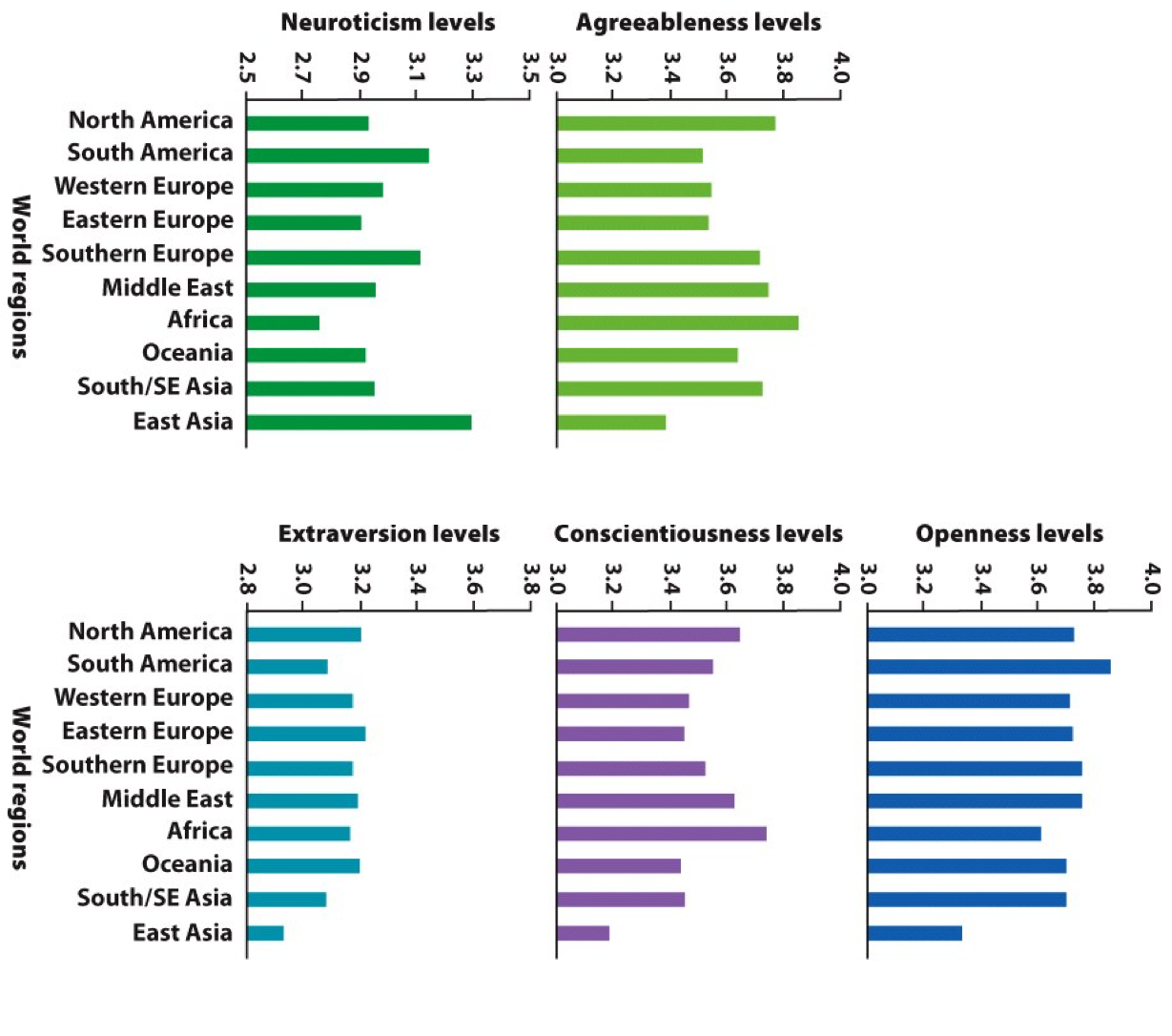
- The maturity principle: increases in agreeableness and conscientiousness, decreases in neuroticism into middle age
The Big Five in animals
- Just like humans, nonhuman animals display consistent individual differences in behaviors across settings and circumstances
- Found in 64 different species
- Personality traits that are most prominent in nonhuman animals
- Extraversion
- Neuroticism
- Agreeableness

Personality Test
-
1 = Disagree strongly, 5 = agree strongly
-
I see myself as someone who…
- Is reserved
- Is generally trusting
- Tends to be lazy
- Is relaxed, handles stress well
- Has few artistic interests
- Is outgoing, sociable
- Tends to find fault with others
- Does a thorough job
- Gets nervous easily
- Has an active imagination
Mine
- I see myself as someone who…
- Is reserved = 5
- Is generally trusting = 3
- Tends to be lazy = 4
- Is relaxed, handles stress well = 3
- Has few artistic interests = 2
- Is outgoing, sociable = 1
- Tends to find fault with others = 5
- Does a thorough job = 5
- Gets nervous easily = 5
- Has an active imagination = 5
Vocab
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| oral stage | stage of development in which the child becomes less dependent on caretakers |
| oral stage (stingy mom) | personality described by pessimism, envy, suscpicion and sarcasm |
| oral stage (over indulgent mom) | personality described by optimistic, gullible, and full of admiration for others |
| anal stage | stage of development which arises around the age of toilet training. Child has learn to control bodily needs which leads to a sense of accomplishment and independence |
| anal-expulsive personality | messy, wasteful, or destructive personality |
| anal-retentive personality | a stringent, orderly, rigid and obsessive personality |
| castration anxiety | The idea that a young boy seeing a naked woman would think they were castrated and then act like their dad out of fear |
| phallic character | reckless, resolute, self-assured, and narcissistic personality |
| phallic stage | stage of development described by oedipus complex, castration anxiety, and penis envy |
| latency period | stage of development in which there is no conflict and person’s ego and superego develop more |
| genital stage | Stage of development in which there is no conflict and the goal is to become a well balanced, healthy person |
| humanistic approach | seeks to undersstand personality by focusing on how people seek to fulfil their potential through greater self-understanding |
| peak experiences | rare moments of rapture caused by the attainment of excellence or the experience of beauty |
| trait approaches | focus on how individuals differ in personality dispositions, such as sociability, cheerfulness, and aggressiveness |
| five-factor model | predicts behavior of people by identifying five basic personality traits |
| the big five | openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and nueroticism |