Week 6 - Day 3
Navigate using audio
-
Clicker lightning round
- What is TiCO_3?
- Titanium (II) carbonate
- Audio 0:01:48.045761
- Give the formula for sodium perchlorate
- NaClO_4
- Give the name for NaSO_3
- sodium bisulfite
- (SO_3 = sulfite)
- sodium bisulfite
- Give the name for KMnO_4
- Potassium permanganate
Covalent Bonding
- Audio 0:04:33.001883
Covalent Bonding: Bonding and Lone Pair Electrons
- Audio 0:05:07.718537
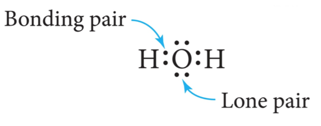
- Electrons that are shared by atoms are called bonding pairs.
- Electrons that are not shared by atoms but belong to a particular atom are called lone pairs.
- Also known as nonbonding pairs
- Audio 0:06:48.740545
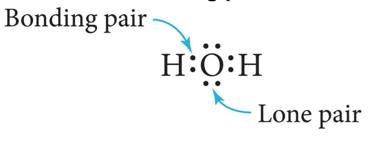
- The top and bottom electrons on the O atom are lone pairs
Single Covalent Bonds
- Audio 0:07:48.556923
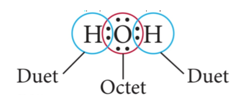
- When two atoms share one pair of electrons, the result is called a single covalent bond.
- Two electrons
- One atom may use more than one single bond to fulfill its octet.
- To different atoms + H only duet
Double Covalent Bond
- Audio 0:09:16.705706
- When two atoms share two pairs of electrons, the result is called a double covalent bond.
- Four electrons between the two atoms
- Example: O2

- Audio 0:10:33.321892
- Elements that can double-bond with each other and themselves are C, N, O, S, and P
Triple Covalent Bond
- Audio 0:11:13.222743
- When two atoms share three pairs of electrons, the result is called a triple covalent bond.
- Six electrons between the two atoms
- Example: N2

- Elements that can triple-bond with each other and themselves are C, N, O, and S.
Covalent Bonding: Model versus Reality
- Audio 0:13:08.879773
- Lewis theory
- implies that some combinations should be stable, whereas others should not. + Stable combinations result in “octets.”
- allows us to predict the formulas of molecules of covalently bonded substances.
+ Hydrogen and the halogens are all diatomic molecular elements, as predicted by Lewis theory.
+ Oxygen generally forms either two single bonds or a double bond in its molecular compounds.
- There are some stable compounds in which oxygen has one single bond and another in which it has a triple bond, but it still has an octet.
Covalent Bonding: Model versus Reality
- Audio 0:14:51.981353
- Lewis theory of covalent bonding
- implies that the attractions between atoms are directional. + The shared electrons are most stable between the bonding atoms.
- predicts that covalently bonded compounds will be found as individual molecules.
+ Rather than an array like ionic compounds
- Compounds of nonmetals are made of individual molecule units.
Molecular Compounds: Formulas and Names
- Audio 0:16:15.133336
- Molecular compounds are composed of two or more nonmetals.
- The formula for a molecular compound cannot readily be determined from its constituent elements because the same combination of elements may form many different molecular compounds, each with a different formula.
- Nitrogen and oxygen form all of the following unique molecular compounds:
- NO, NO2, N2O, N2O3, N2O4, and N2O5.
Molecular Compounds
- Audio 0:17:43.500253
- Names of Molecular Compounds:
- Write the name of the element with the smallest group number first.
- If the two elements lie in the same group, then write the element with the greatest row number first.
- The prefixes given to each element indicate the number of atoms present.
Binary Molecular Compounds
- Audio 0:18:59.257994

- These prefixes are the same as those used in hydrates:
| Prefix | Number |
|---|---|
| mono | 1 |
| di | 2 |
| tri | 3 |
| tetra | 4 |
| penta | 5 |
| hexa | 6 |
| hepta | 7 |
| octa | 8 |
| nona | 9 |
| deca | 10 |
- If there is only one atom of the first element in the formula, the prefix mono- is normally omitted
Molecular Compounds
- Audio 0:20:34.443243
| molecule | name |
| HI | hydrogen iodide |
| NF_3 | nitrogen trifluoride |
| SO_2 | suffer dioxide |
| N_2Cl_4 | dinitrogen tetrachloride |
| NO_2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| N_2O | dinitrogen monoxide |
Mass
- Audio 0:23:26.555568
- Molecular mass (or molecular weight) is the sum of the atomic masses (in amu) in a molecule
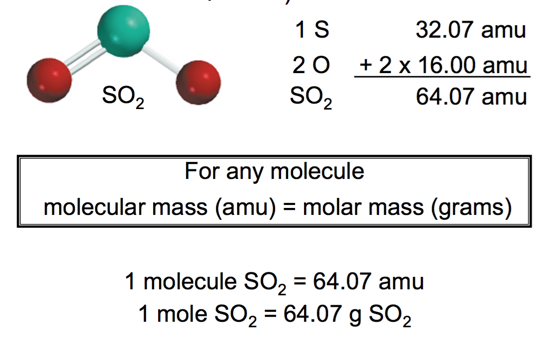
Another Molecular Mass Example
- Audio 0:25:48.242857
- What is the Molecular Mass of C3H8O ?
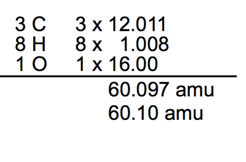
Clicker question
- Find the molecular weight of urea (CH4N2O)
- (All but 1% got it right)
Using Molar Mass to Count Molecules by Weighing
- Audio 0:28:43.992973
- Molar mass in combination with Avogadro’s number can be used to determine the number of atoms in a given mass of the element.
- Use molar mass to convert to the amount in moles. Then use Avogadro’s number to convert to number of molecules.
+

Using Molecular Mass
- Audio 0:39:35.097586
- How many H atoms are in 72.5 g of C3H8O ?
- Mass percent composition of an element in a compound =

- n is the number of moles of the element in 1 mole of the compound

- Audio 0:42:11.330892
- What is the mass percent of Ca in CaCl2
- CaCl2 (Ca = 40.08, Cl = 35.45)
Clicker 3
- Audio 0:44:25.808433
Vocab
| term | Definition |
|---|---|
| bonding pairs | Electrons that are shared by atoms |
| lone pairs (nonbonding pairs) | Electrons that are not shared by atoms but belong to a particular atom |
| single covalent bond | when two atoms share one pair of electrons |
| double covalent bond | when two atoms share two pairs of electrons |
| triple covalent bond | when two atoms share three pairs of electrons |