Week 10 - Day 2
Navigate using audio
Announcements
- Audio 0:00:49.845897
- NOYCE Presentation
- Summer Internship for year 1
- Pays money
- $1350 for 3 weeks (Deadline April 6, 2017)
- Noyce Program
- Asks you to teach while you go to school
How Many Moles of CO2 Form If 22.0 Moles of C8H18 Are combusted (Burned)?
- Audio 0:06:51.877125
Mole-to-Mass and Mass-to-Mass Conversions
- Audio 0:17:07.273524
- 2 C8H18(l) + 25 O2(g) → 16 CO2(g) + 18 H2O(g)
- Problem:
- Determine the mass (grams) of CO2 produced when 3.6 × 1015 grams of C8H18 is burned in excess oxygen gas.
- Strategy:
- Need a balanced reaction
- From the balance reaction, use the stoichiometric relationship between C8H18 and CO2.
- Mass of C8H18 → Moles of C8H18 → Stoichiometric ratio 2 C8H18 : 16 CO2 → Moles of CO2 → Mass of CO2
Problem: Determine the mass (grams) of CO2 produced when 3.6 × 1015 grams of C8H18 is burned in excess oxygen gas.
- Audio 0:19:15.117851
- 2 C8H18(l) + 25 O2(g) → 16 CO2(g) + 18 H2O(g)
Practice Problem: Stoichiometry plants produce glucose (C6H12O6) from CO2 and water. How much glucose can a plant produce from 37.8 g CO2
- Audio 0:21:44.744416
Limiting Reactant, Theoretical Yield
- Audio 0:28:22.489586
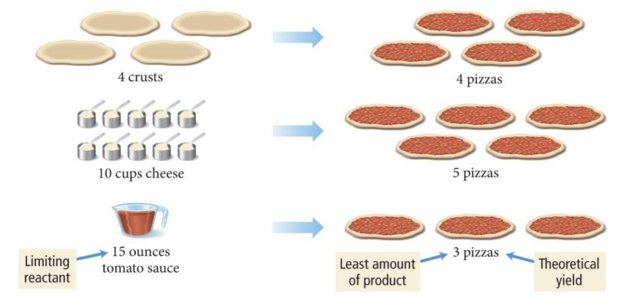
- Back to the pizza recipe:
- 1 crust + 5 oz. tomato sauce + 2 cups cheese → 1 pizza
- Suppose you have 4 crusts, 10 cups of cheese, and 15 oz. tomato sauce. How many pizzas can you make?
- Strategy:
- We have enough crusts to make
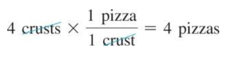
- We have enough cheese to make
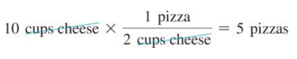
- We have enough tomato sauce to make

- If you are given two or more quantities or reactants, then it is a limiting reagent problem
Limiting Reactant: Pizza Problem Continued
- We have enough crusts for 4 pizzas, enough cheese for 5 pizzas, but ONLY enough tomato sauce for 3 pizzas.
- Therefore, only 3 pizzas can be made.
- The tomato sauce limits how many pizzas can be made.
Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield Connection
- Audio 0:32:11.720988
- In the pizza analogy, the tomato sauce is the limiting reactant, the reactant that makes the least amount of product.
- The limiting reactant is also known as the limiting reagent.
- The maximum number of pizzas that can be made depends on this ingredient, the tomato sauce.
- In chemical reactions, this is called the theoretical yield.
- Theoretical yield is the amount of product that can be made in a chemical reaction based on the amount of limiting reactant.
- Example:
- The ingredient that makes the least amount of pizza determines how many pizzas you can make (theoretical yield).
- Example:
More Making Pizzas
- Audio 0:33:57.386964
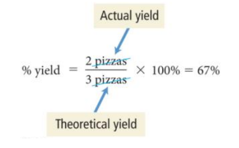
- Assume that while making pizzas, a pizza is burnt or dropped on the floor and only two pizzas are available to eat.
- The actual amount of product made in a chemical reaction is called the actual yield.
- Actual yield is about efficiency.
- To determine your efficiency in making pizzas, a percentage value can be calculated.
- In chemical reactions, this is called a percent yield.
Summarizing Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield
- Audio 0:35:14.485560
- The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction and limits the amount of product.
- The reactant in excess is any reactant that occurs in a quantity greater than is required to completely react with the limiting reactant.
- The theoretical yield is the amount of product that can be made in a chemical reaction based on the amount of limiting reactant.
- The actual yield is the amount of product actually produced by a chemical reaction.
- The percent yield is calculated as:
- (actual yield /theoretical yield) × 100 = percent yield%
Chemical Reaction
- In reactions with multiple reactants, it is likely that one of the reactants will be completely used before the others.
- When this reactant is used up, the reaction stops and no more product is made.
- The reactant that limits the amount of product is called the limiting reactant.
- It is sometimes called the limiting reagent.
- The limiting reactant gets completely consumed.
- Reactants not completely consumed are called excess reactants.
- The reactant in excess is any reactant that occurs in a quantity greater than is required to completely react with the limiting reactant.
- The amount of product that can be made from the limiting reactant is called the theoretical yield.
Practice Problem: Stoichiometry—Limiting Reactant and Theoretical Yield
- Audio 0:36:18.679366
- Ammonia, NH3, can be synthesized by
- 2NO(g) + 3H2(g) è 2NH3(g) + 2H2O(g)
- Starting with 86.3 g NO and 25.6 g H2, find the theoretical yield of NH3
What is the percent yield of C2H2 if 62.80 g of water yields 15.38 g of C2H2 using the following equation.
- Audio 0:46:17.094052
- CaC2(s) + 2 H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + C2H2(g)
- A) 13.84%
- B) 33.90%
- C) 91.47%
- D) 48.10%
- E) 68.52%
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| limiting reactant | the reactant that makes the least amount of product |
| theoretical yield | the amount of product that can be made in a chemical reaction based on the amount of limiting reactant |
| actual yield | the actual amount of product made in a chemical reaction |
| percent yield | the efficiency percentage of how much product is made in a chemical reaction (Calculated as 100 * actual yield / theoretical yield ) |
| excess reactants | reactants not completely consumed are called |