Week 11 - Day 2
Navigate using audio
- Audio 0:04:20.568986
Clicker 1
- How many molecules of sucrose (C12H22O11, molar mass = 342.30 g/mol) are contained in 14.3 mL of 0.140 M sucrose solution
- A) 8.29 * 10^22 molecules C12H22O11
- B) 1.21 * 10^21 molecules C12H22O11
- C) 6.15 * 10^22 molecules C12H22O11
- D) 1.63 * 10^23 molecules C12H22O11
- E) 5.90 * 10^24 molecules C12H22O11
Solution Stoichiometry
- Audio 0:07:44.395193
- Molarity (moles solute/liter of solution) relates the moles of solute to the liters of solution.
- Molarity can be used to convert between amount of reactants and/ or products in a chemical reaction when either the reactant or product is given in volume.
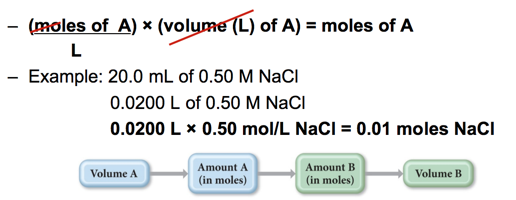
- Example: 20.0 mL of 0.50 M NaCl
- Molarity of A × Volume of A = moles A
Practice Problem: Solution Stoichiometry
- Audio 0:08:39.470935
-
What volume (in L) of 0.150 M KCl solution will completely react with 0.150 L of a 0.175 M Pb(NO3)2 solution?
Clicker 2
- Audio 0:16:26.983035
- What volume of 0.244 M KCl solution is required to react exactly with 50.0 mL of 0.210 M PB(NO3)2 solution?
- A) 97.4 mL
- B) 116 mL
- C) 43.0 mL
- D) 86.1 mL
- E) 58.1 mL
Types of Aqueous Solutions and Solubility
- Audio 0:20:31.538420
- You can’t add infinite amounts of solute to your solution
- Consider two familiar aqueous solutions: salt water and
sugar water.
- Salt water is a homogeneous mixture of NaCl and H2O.
- Sugar water is a homogeneous mixture of C12H22O11 and H2O.
- How do solids such as salt and sugar dissolve in water?
- Likes dissolve likes.
- If your solute has roughly similar properties to your solvent, it will dissolve
What Happens When a Solute Dissolves?
- Audio 0:23:19.196102
- There are attractive forces between the solute particles holding them together.
- There are also attractive forces between the solvent molecules.
- When we mix the solute with the solvent, there are attractive forces between the solute particles and the solvent molecules.
- If the attractions between solute and solvent are strong enough, the solute will dissolve.

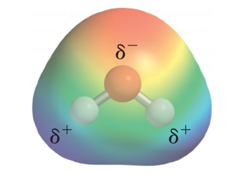
Charge Distribution in a Water Molecule
- Audio 0:25:45.466724
- There is an uneven distribution of electrons
within the water molecule.
- This causes the oxygen side of the molecule to have a partial negative charge (δ–) and the hydrogen side to have a partial positive charge (δ+).
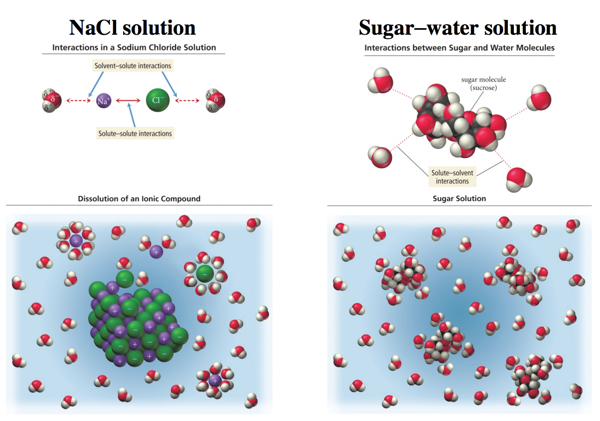
Solute and Solvent Interactions in an Ionic Solution: A Salt Solution
- Audio 0:26:59.261993
- When sodium chloride is put into water, the attraction of Na+ and Cl– ions to water molecules competes with the attraction among the oppositely charged ions themselves.
- Sodium chloride is an ionic compound (metal + nonmetal).
- Ionic compounds when dissolved in water are called salt solutions.

Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Dissolving in Water
- Each ion is attracted to the surrounding water molecules and pulled off and away from the crystal.
- When it enters the solution, the ion is surrounded by water molecules, insulating it from other ions.
- The result is a solution with free moving charged particles able to conduct electricity.

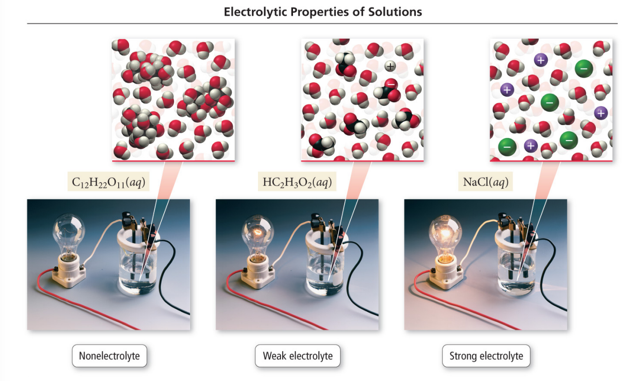
Electrolyte and Nonelectrolyte Solutions
- Audio 0:29:17.039172
- Materials that dissolve in water to form a solution that will conduct electricity are called electrolytes.
- Materials that dissolve in water to form a solution that will not conduct electricity are called nonelectrolytes.
- A solution of salt (an electrolyte) conducts electrical current. A solution of sugar (a nonelectrolyte) does not.
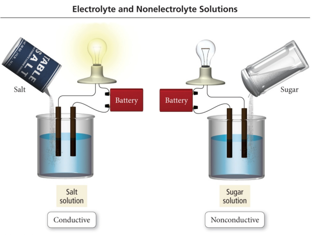
Salt versus Sugar Dissolved in Water NaCl solution Sugar–water solution
Electrolyte Solutions: What Are They?
- Audio 0:31:02.947720
- Electrolytes are classified by how they dissolve in water.
- If their dissociation is into ions:
- Strong electrolytes
- Completely dissociate into ions
- Example: CaCl2(s) → Ca2+ + 2 Cl−
- Weak electrolytes
- Partial dissociation into their ions
- Example: HCOOH(aq) H+ + HCOO−
- Strong electrolytes
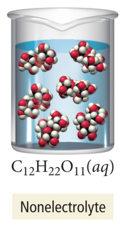
- Molecular compounds that dissolve in water but do not form ions when they go into solution are called nonelectrolytes.
- If their dissociation is into ions:
Electrolyte Solutions: Strong and Weak
- Audio 0:32:53.074436
- Ionic substances such as sodium chloride (NaCl) that completely dissociate into ions when they dissolve in water are strong electrolytes.
- Acids are compounds that when dissolved in water dissociate to give H+
- Bases are compounds that when dissolved in water dissociate to give OH-
- Depending on the acid or base, their dissociation in water can be complete or partial.
- Example:
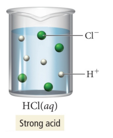
- HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid is a strong acid.
- It dissociates completely in water.
- HCl would be a strong electrolyte.
- It dissociates completely in water.
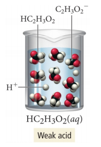
- Acetic acid (e.g., vinegar) (HC2H3O2) is a weak acid—it dissociates partially in water.
- HC2H3O2 is a weak electrolyte.
- HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid is a strong acid.
- Example:
Clicker 3
- Audio 0:36:58.662109
- Which of the following will have the highest electrical conductivity?
- A) 0.045 M Al2(SO4)3
- B) 0.050 M (NH4)2CO3
- C) 0.10 M NaBr
- D) 0.10 M Kl
- E) 0.10 M KF
Electrolyte and Nonelectrolyte Solutions
- Sugar (C12H22O11) is a molecular compound.
- Most molecular compounds (except for acids and bases) dissolve in water as intact molecules.
- Nonelectrolyte solution
- Most molecular compounds (except for acids and bases) dissolve in water as intact molecules.
Electrolytic Properties of Solution
The Solubility of Ionic Compounds
- Audio 0:39:50.836785
- When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the resulting solution contains:
- Not the intact ionic compound itself, but its component ions dissolved in water
- NOT all ionic compounds dissolve in water.
- Example:
- If we add AgCl to water, for example, it remains solid and appears as a white powder at the bottom of the water.
- Example:
- In general, a compound is termed soluble if it dissolves in water and insoluble if it does not.
Solubility of Salts
- Audio 0:41:22.482755
- If solid silver nitrate (AgNO3) is added to water, it dissolves and forms a strong electrolyte solution.
- Silver chloride (AgCl), on the other hand, is almost completely insoluble.
- If solid AgCl is mixed with water, virtually all of it remains as a solid within the liquid water.

When Will a Salt Dissolve?
- Audio 0:41:46.575491
- Whether a particular compound is soluble or insoluble depends on several factors.
- Predicting whether a compound will dissolve in water is not easy.
- The best way to do it is to do some experiments to test whether a compound will dissolve in water, and then develop some rules based on those experimental results.
Solubility Rules
- Audio 0:41:59.485417

Practice Problem: Ionic Compound Solubility
- Predict whether each compound is soluble or insoluble
- (a) PbCl2
- (b) CuCl2
- (c) Ca(NO3)2
- (d) BaSO4
Vocab
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| electrolytes | materials that dissolve in water to form a solution that will conduct electricity |
| nonelectrolytes | materials that dissolve in water to form a solution that will not conduct electricity are called |
| acids | compounds that when dissolved in water dissociate to give H+ |
| bases | compounds that when dissolved in water dissociate to give OH- |
| soluble | compound which dissolves in water |