Week 5 - Day 1 (Transition to Old Age)
Social Influence
- Who is more influential during adolescence, parents or friends?
The Transition to Old Age
- Questions people ask themselves:
- Is it okay to be who I was?
- Become isolated easier
- Less connected
- People are living longer
- The number of people over age 85 is growing dramatically
- Better medicine
The elderly contribute much to modern society
- Many older adults work productively well past their 70s
- Supreme court Most are over the age of 85
- Morgan Freeman Still acting
- Paul Simon
- Still touring
Deterioration
- The body and mind start deteriorating slowly at about age 50
- Adolescents continue growing until your 25
- Your brain stops growing after this
- 50 starts going backward
- Adolescents continue growing until your 25
- Trivial physical changes include the graying and whitening of hair and the
wrinkling of skin
- Surface level changes
- Some of the most serious changes affect the brain, where frontal lobes shrink proportionally more than other brain regions
- Frontal lobes are center of higher cognitive thought
- Explains why older people have trouble remembering things or keeping up with things and learning new technologies
- Exacerbated in some individuals
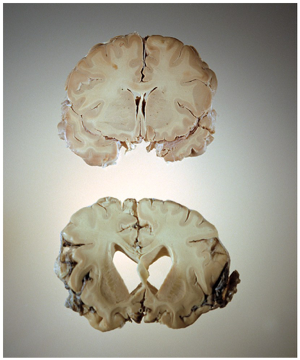
- The brain of someone with Alzheimer’s has physically afflicted brain
- Where you would normally find the hippocampus, there is nothing there ## Cognitive changes
- It is difficult to pinpoint the causes of cognitive decline in old age
- Perhaps if someone older stops reading, their brain loses some strength
- The frontal lobes, which play an important role in working memory and many other cognitive skills, typically shrink as people grow older
- People with impaired hearing won’t participate in conversation because they lose the ability to engage as much
- Causes a more general decline in mental ability
- People with impaired hearing won’t participate in conversation because they lose the ability to engage as much
- Types of changes
- Slowing of mental processing speed
- Sensory-perceptual changes
- Sensitivity to sensory information
- Someone driving really slow might be worried because they are processing sensory information slower ## Changes in Memory
- Long-term memory is less affected by aging than is working memory
- Childhood stories are safe
- Working memory includes someone telling you their phone number
- Usually stays in a normal brain for a minute, then it’s gone
- Multitasking suffers
- Older people often need more time to learn new information
- Once they learned, they use it as efficiently as younger people
- Especially true for recognition tasks
- One reason for the decline in memory related to aging is that older adults tend not to use strategies that facilitate memory
- They don’t have life-styles that promote learning
- They have a routine often
- Eat and do the same things every day
- Another reason for declines in working memory is age-related reductions in dopamine activity in the frontal lobes
- Dopamine is related to reward
- Not as rewarded by environmental stimuli ## Changes in Intelligence
- Research has indicated consistently that intelligence, as measured on standard psychometric tests, declines with advanced age
- They have a harder time with IQ tests
- Fluid intelligence vs. Crystallized intelligence
- Fluid intelligence refers to the ability to process new general information without specific prior knowledge
- IQ requires fluid
- This is analyzing something you’ve never seen before and finding a solution
- Crystallized intelligence refers to specific knowledge that must be learned or memorized
- Things you’ve already learned
- Older people excel at this
- Older people can even grow this
- Things you’ve already learned
- Fluid intelligence refers to the ability to process new general information without specific prior knowledge
- Crystallized intelligence usually increases throughout life
- Although memory and the speed of processing may decline, the continued ability to learn new information may mitigate those losses in terms of daily functioning ## Positive Changes in Adulthood
- Except for dementia, older adults have fewer mental health problems, including depression, than younger adults
- Most are pretty content
- Even with chronic or daily pain, most end up happier
- Socioemotional selectivity theory
- As people grow older, they perceive time to be limited
- As a result, they adjust their priorities to emphasize emotionally meaningful events, experiences, and goals
- Older people show better memory for positive than for negative information
Vocab
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Fluid Intelligence | refers to the ability to process new general information without specific prior knowledge |
| Crystallized intelligence | refers to specific knowledge that must be learned or memorized |
| Socioemotional selectivity | theory that as people grow older, they begin to see time as limited and adjust their priorities |