Week 10 - Day 2 Mental Health Treatment
Navigate using audio
Quizlet on terms from this lecture
Audio 0:01:30
Mental Health Providers
-
Clinical Psychologist
-
Has a Ph.D. or Psy.D.
-
Is skilled in working with individuals with mental illness
-
Counseling Psychologist
-
Audio 0:02:30
-
Has a Ph.D.
-
Deals with adjustment problems that do not involve mental illness
-
Handles general problems
-
Psychiatrist
-
Has an M.D.
-
Can prescribe psychotropic medicatoins
-
Audio 0:05:05
-
Do these roles overlap?
Two Basic Forms of Treatment
Audio 0:06:18
-
Psychotherapy: formal psychological treatment
-
Techniques depend on practitioner’s training
-
All forms involve interaction between practitioner and client
-
Goal is to help the client understand his or her symptoms and provide solutions
-
Biological therapies: based on medical approaches to illness and disease
-
Predicated on the notion that mental illness results from abnormalities in neural and bodily processes
-
Psychopharmacology: the use of medications that affect brain or bodily functions
Audio 0:07:46
Types of therapies
-
Psychodynamic
-
Humanistic
-
Cognitive & Behavioral
-
Group Therapy
-
Family Therapy
Audio 0:08:22
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychoanalysis
-
Free association
-
Dream analysis
-
Focus on the unconscious
Aim is to help the patient gain insight into his or her psychological processes
-
Transference:
-
The unconscious projection of emotions or reactions onto the therapist
-
Audio 0:10:27
-
Used somewhat today. Not a whole lot
-

Humanist Therapy
-
Focus on the whole person
-
Goal is to treat the person a whole, not as a collection of behaviors or a repository of repressed thoughts
-
Client-centered therapy: encourages people to fulfill their individual potentials for personal growth through greater self-understanding
-
Therapists strive to create a safe and comforting setting for clients to access their true feelings, to be empathic, and to accept the client through unconditional positive regard
-
Audio 0:13:35
-
Therapist will often use reflective listening
-
Audio 0:13:46
Audio 0:15:31
Cognitive and Behavioral Therapies
-
Behavior Therapy
-
Based on two ideas:
-
Behavior is learned
-
Behavior can be unlearned through classical and operant conditioning
-
Appropriate behaviors are learned through modeling
-
Forms
-
Systematic desensitization
-
CS → CR1 (fear) connection
-
Replaced with: CS → CR2 (relaxation) connection
Audio 0:17:50
-
Behavior Therapy
-
Forms (continued)
-
Graduated exposure
-
Gradual exposure to feared situations, feared objects, or traumatic memories until fear subsides
-
Behavioral self-monitoring
-
Carefully monitoring the frequency and consequences of the target behavior
-
Cognitive Therapy
-
Based on the idea that distorted thoughts can produce maladaptive behaviors and emotions
-
Treatment strategies attempt to modify these thought patterns to produce emotional and behavioral results
-
Forms
-
Rational-emotive therapy
-
The therapist acts as a teacher, explaining errors in thinking and demonstrating more productive ways to think and behave
-
Cognitive restructuring
-
Audio 0:21:00
-
A clinician seeks to help a client recognize maladaptive thought patterns and replace them with more appropriate ways of viewing the world
Patterns of thinking
-
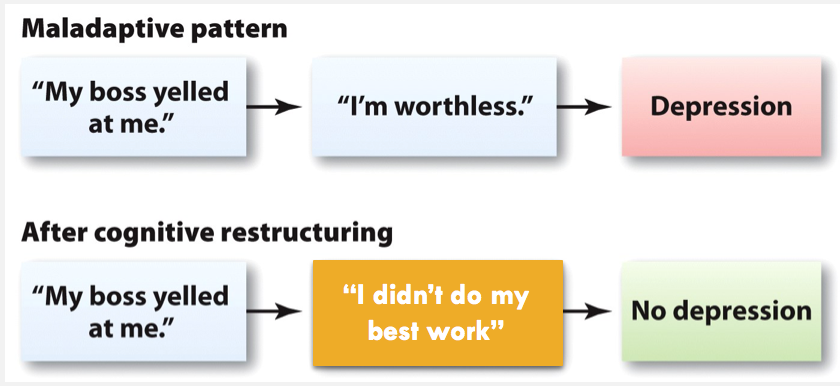
-
Audio 0:23:00
Cognitive & Behavioral Therapies (Cont)
Audio 0:24:00
-
Cognitive Therapy
-
Forms (continued)
-
Interpersonal therapy
-
Focuses on circumstances (i.e., relationships)
-
Tries to help clients explore their interpersonal experiences and express their emotions
-
Mindfulness-based therapy
-
Intended to prevent relapse into mental illness
-
Has two goals: (1) help clients be aware of negative thoughts and feelings during vulnerable moments, and (2) help clients avoid ruminative thinking through meditation
-
Audio 0:26:00
-
Similar to self-mutilation in ways
-
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Group Therapy
Audio 0:27:30
-
Group therapy builds social support
-
Advantages
-
Often significantly less expensive than individual treatment
-
Group setting provides an opportunity for members to improve their social skills and learn from one another’s experiences
-
Insurance reasons too
-
Audio 0:28:37
-
Many groups are organized around a particular type of problem or around a particular type of client
-

-
Fight club
-
Therapy might be highly structured, or a more loosely organized forum for discussion
Audio 0:30:00
Family Therapy
-
According to a family-systems perspective, an individual is part of a larger context where changes in individual behavior will affect the whole system
-
Example: The level of expressed emotion from family members corresponds to the relapse rate for patients with schizophrenia (Hooley & Gotlib, 2000)
-
Audio 0:31:50
-
Offers the opportunity to change attitudes and behaviors that are disruptive to the family
-

Biological Treatment - Medication
-
Psychotropic medications affect mental processes
-
Effective for certain disorders
-
Anti-anxiety drugs decrease anxiety by increasing activity of GABA
-
Antidepressants decrease depression by increasing availability of serotonin and other neurotransmitters
-
Antipsychotic drugs reduce psychotic symptoms by blocking effects of dopamine
Alternative Biological Treatments
-
Used in extreme cases
-
Examples:
-
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): a procedure that involves administering a strong electrical current to the patient’s brain to produce a seizure
-
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): a powerful electrical current produces a magnetic field that when rapidly switched on and off induces an electrical current in the brain interrupting neural functioning in a certain region
-
Audio 0:38:46 (about to watch video)
-
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): electrodes are surgically implanted deep within the brain; mild electricity is then used to stimulate the brain at an optimal frequency and intensity
Vocab
| Clinical Psychologist | Psychologist who is skilled in working with individuals with mental illness (has a Ph.D) |
|
Counseling Psychologist |
Psychologist who deals with general problems with individuals who do not have mental illness (has a Ph.D) |
|
Psychiatrist |
Psychologist who can prescribe psychotropic medications |
|
Psychotherapy |
formal psychological treatment |
|
Biological therapies |
Based on medical approaches to illness and disease |
|
Psychopharmacology |
the use of medications that affect brain or bodily functions |
|
Transference |
The unconscious projection of emotions or reactions onto the therapist |
| Humanist therapy | Form of therapy which tries to focus on the whole person |
|
Client-centered therapy |
Form of therapy which encourages people to reach their full potential (subset of humanist therapy) |
| reflective listening | When someone responds to you with their interpretation of what you say |
|
Behavior therapy |
A form of therapy where the therapist shows the patient how to respond in specific situations through example |
| Graduated exposure | Form of behavioral therapy which gradually introduces a patient to feared stimulus |
| Cognitive therapy | Therapy based on the idea that distorted thoughts can produce maladaptive behaviors |
|
Cognitive restructuring |
Part of cognitive therapy which aims to train the patient to recognize bad behavior |
|
Interpersonal therapy |
Form of cognitive therapy which focuses on circumstances (relationships) |
|
Mindfulness-based therapy |
Form of cognitive therapy which aims to make you release your thoughts |
|
Group therapy |
A form of therapy which builds social support |
|
Anti-anxiety drugs |
decrease anxiety by increasing activity of GABA |
|
Antidepressants |
decrease depression by increasing availability of serotonin and other neurotransmitters |
| Antipsychotic drugs | reduce psychotic symptoms by blocking effects of dopamine |
|
Electroconvulsive therapy |
Form of alternative therapy in which a shock is administered to your body and causes you to have a seizure (it is not known why this works) |
|
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation |
Form of alternative therapy in which a powerful current produces a magnetic field which turns on and off and interrupts neurological function in a specific brain region |