Week 15 - Day 1 (Ch 2 pt 3 - Personality)
Navigate using audio
Anouncements
- Email screenshot of SOI with “SOI” in the subject line
Theories of Personality pt 3
ICA #14 (From last time)
Personality Test
-
1 = Disagree strongly, 5 = agree strongly
-
I see myself as someone who…
- Is reserved
- Is generally trusting
- Tends to be lazy
- Is relaxed, handles stress well
- Has few artistic interests
- Is outgoing, sociable
- Tends to find fault with others
- Does a thorough job
- Gets nervous easily
- Has an active imagination
Mine
- I see myself as someone who…
- Is reserved = 5
- Is generally trusting = 3
- Tends to be lazy = 4
- Is relaxed, handles stress well = 3
- Has few artistic interests = 2
- Is outgoing, sociable = 1
- Tends to find fault with others = 5
- Does a thorough job = 5
- Gets nervous easily = 5
- Has an active imagination = 5
Scores
- R = reverse
- N = normal
- (R; 1=5, 2=4, 3=3, 4=2, 5=1)
- R
- N
- R
- R
- R
- N
- R
- N
- N
- N
My score
- = 1 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 1 + 1 + 5 + 5 + 5
- = 30
- Audio 0:06:17.906329
Where does personality come from?
Genetic vs. learned?
- Temperament
- Physiological disposition to respond to the environment in certain ways
- Audio 0:08:16.491145
- Present in infancy, assumed to be innate
- To some extent genetic
- Relatively stable over time
- Audio 0:09:12.580248
- Physiological disposition to respond to the environment in certain ways
- Includes…
- Reactivity
- Soothability
- Audio 0:09:35.591669
- Positive and negative emotionality
Heritability of personality
- Heritability
- A statistical estimate of the proportion of the total variance in some trait that is attributable to genetic differences among individuals within a group
- Heritability of personality traits is about 50 percent
- Within a group of people, about 50 percent of the variation associated with a given trait is attributable to genetic differences among individuals in the group
- The rest is environment
- Genetic predisposition is not genetic inevitability
Environmental influences
- Non-shared environment: unique aspects of a person’s environment and experience that are not shared with family members
- Partially explains why siblings raised in the same home would not have identical personalities
- Not every encounter each sibling has is shared by the other(s)
- Culture
- individualist vs. collectivist
- agricultural vs herding society -> “culture of honor” -> aggressiveness
- Life experiences and role changes
- Audio 0:19:22.921496
- Going to college, job responsibilities, traveling, long-term relationships, having children, etc.
- (In a different study / different graph)
- A study found that southern people have a stronger physiological reaction to altercation
- Audio 0:25:40.192140
- When called an asshole, they had significantly higher cortisol levels than the northern subjects.
- Audio 0:25:40.192140
- A study found that southern people have a stronger physiological reaction to altercation
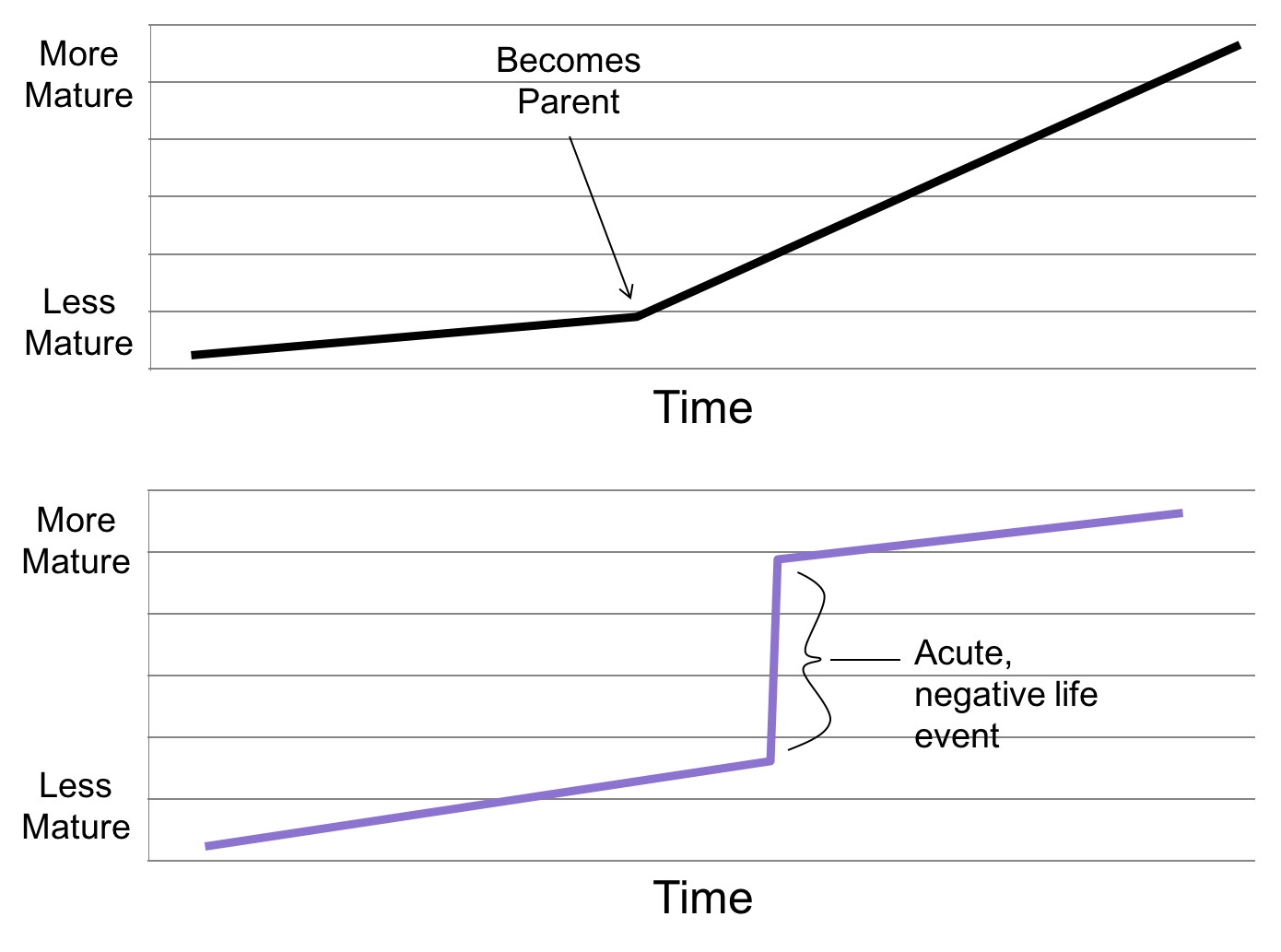
- Audio 0:28:07.183955
- Graph shows that you might have an abrupt spike in maturity after a traumatic or serious life event.
- I.E becoming a parent gives you a slower spike
- Being exposed to a disaster like the April 27th tornado makes you spike in maturity all at once.
- Graph shows that you might have an abrupt spike in maturity after a traumatic or serious life event.
- Audio 0:28:07.183955
Strong Situation

- Audio 0:31:06.283555
Weak Situation

- Audio 0:31:43.605402
Interaction of Personality and Situation
- Reciprocal determinism
- Two-way interaction between aspects of the environment and aspects of the individual in the shaping of personality traits
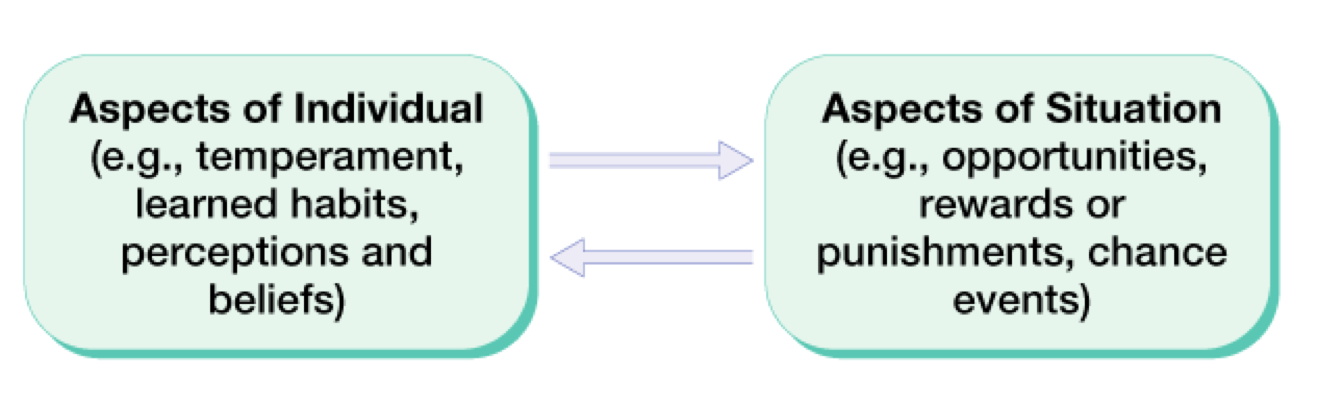
- Ultimately, personality reflects:
- A person’s underlying disposition
- The activation of the person’s goals in a particular situation
- The activation of the person’s emotional responses in the pursuit of those goals
ICA #15
- Audio 0:35:11.324360
- In psychoanalysis, the part of the personality that represents reason, good sense, and rational self-control is called
A. libido
B. the ego
C. the superego
D. the id
- B
- Howard’s psychologist asks him to take a personality test. The test consists of a series of standardized multiple-choice items. The test also includes a section where Howard is asked to rate himself on a series of scales. What type of test is this?
A. projective test
B. objective test
C. Rorschach test
D. humanist test
- B
- __ is a fundamental personality dimension that describes whether people are cooperative and secure, or irritable and abrasive.
A. Agreeableness versus antagonism
B. Extroversion versus introversion
C. Neuroticism versus emotional stability
- A
- In Kaiti’s culture, the wishes of the individual take precedence over group harmony. It is most likely that Kaiti defines her “self” _____.
A. In context of the community
B. In regard to her personality traits
C. In regard to her birth order
D. in the context of her relationships
- B
- In psychoanalysis, the part of the personality that represents reason, good sense, and rational self-control is called
A. libido
B. the ego
C. the superego
D. the id
Chapter 15
- Just-world theory
- The believe that good things happen to good people and bad things happen to bad people
- Cognitive dissonance
- What happens when someone has a belief that conflicts with what they’re being told
- Tend to rationalize it
- What happens when someone has a belief that conflicts with what they’re being told
Motivation
- An inferred process within a person or animal that causes movement either toward a goal or away from an unpleasant situation
- Audio 0:45:17.651855
- Intrinsic Motivation
- The pursuit of an activity for its own sake
- Extrinsic Motivation
- Pursuit of an activity for an external reward (like money)
Vocab
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| temperament | Physiological disposition to respond to the environment in certain ways |
| Heritability | A statistical estimate of the proportion of the total variance in some trait that is attributable to genetic differences among individuals within a group (50%) |
| Non-shared environment | unique aspects of a person’s environment and experience that are not shared with family members |
| Reciprocal determinism | Two-way interaction between aspects of the environment and aspects of the individual in the shaping of personality traits |
| motivation | An inferred process within a person or animal that causes movement either toward a goal or away from an unpleasant situation |